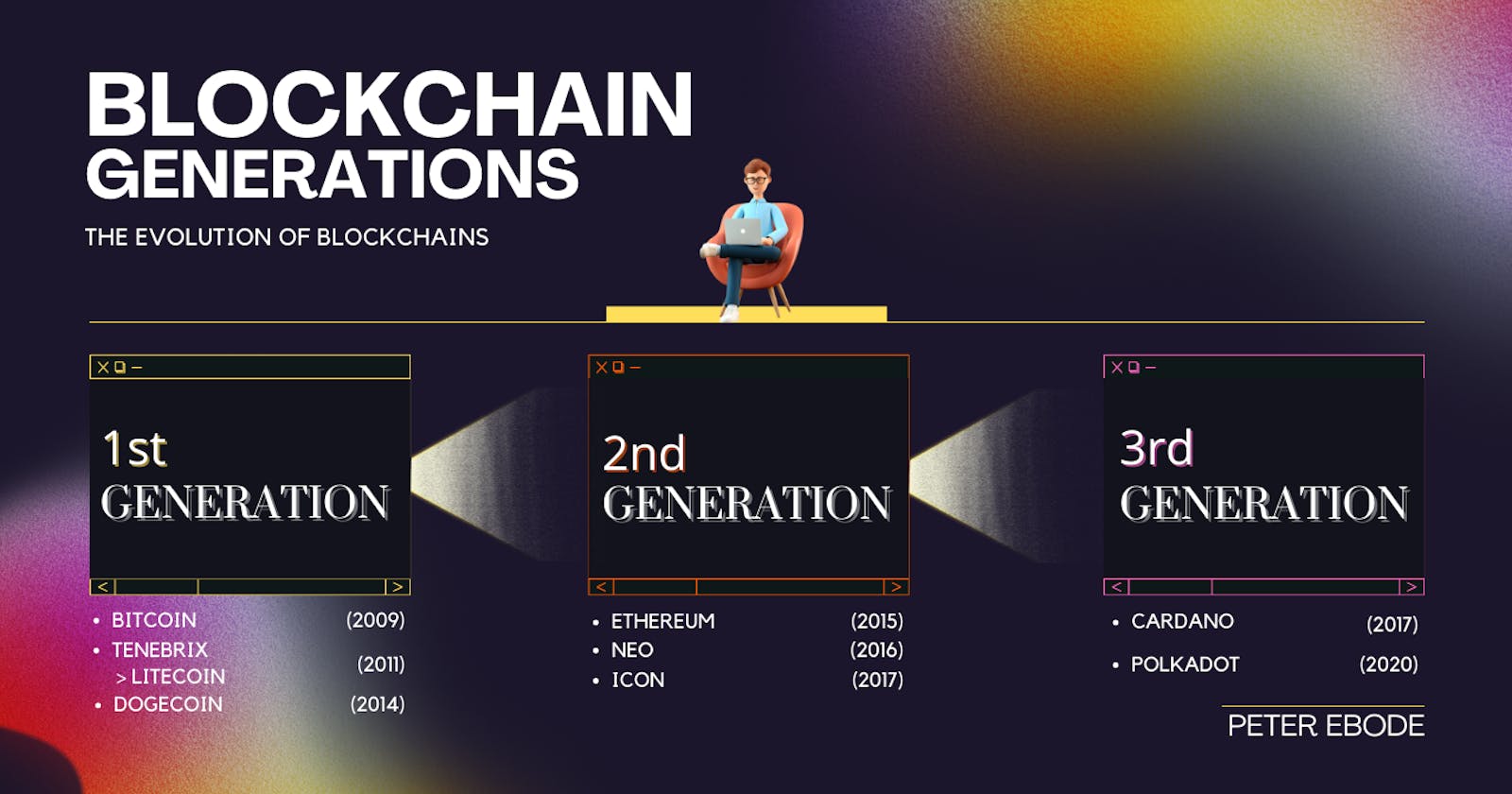
Generations of Blockchain
Tracing the Evolution of Blockchain Technology: From Genesis till now
Art challenges technology and technology inspires art. - John Lasseter (American film director)
I admire one-liner intros, AD does too. It attempts to give an overview of the article, as smoothly as possible, right from the beginning. New technology gets created due to creativity and curiosity or sometimes by accident, we begin to use it, our need from the technology, and our creative use pushes the development of said technology in an almost endless cycle.
The generations of blockchain do not have an explicitly defined milestone, rather it is an observation of how the use case and properties of the blockchain technology have evolved and improved over time.
Each new generation builds on the previous generation and introduces improvement and efficiency to the older generation. In the blockchain space, the first generation made what seemed impossible, possible. The second generation after that built a computer on the chain, the generation we could call the third, brought power efficiency, speed and interoperability improvements into the space. Let's get into more details.
First Generation Blockchains
The first generation of applications on the blockchains, notably Bitcoin and any other chains that adhered to a similar protocol. The Bitcoin blockchain was that one chain that proved that a trustless decentralized monetary system was possible. Its core functionality, rested on the shoulders of cryptography, peer-to-peer networking, and a proof-of-work consensus mechanism specifically, Nakamoto's consensus.
In that generation, it wasn't just bitcoin. Another notable chain developed after Bitcoin was Tenebrix, it imitated bitcoin but changed some functionality under the hood.
TENEBRIX
Tenebrix replaced the SHA-256 rounds in Bitcoin's mining algorithm with the Scrypt function, this would allow Tenebrix to be "GPU-resistant" making it possible for regular people with CPUs to be miners. It never took off, because people criticized the creator for pre-mining 7.7 million Tenebrix(TBX ) for himself at no cost.
Q & A on Tenebrix by the creator from 2011 here
LITECOIN
Charlie Lee, a Google employee at the time created an alternative version of Tenebrix called Fairbrix (FBX) and eventually went on to create Litecoin. Litecoin used the scrypt function, and took other characteristics from Bitcoin, but was faster and had lesser fees.
DOGECOIN
Dogecoin climbed out in the early 2014s, initially released in 2013, it is considered both the first meme coin and more specifically, the first dog coin. It is also based on Scrypt's algorithm, and the transaction process is more convenient than Bitcoin. Dogecoin takes only 1 minute to confirm, while BTC takes 10 minutes.
Second Generation Blockchains
The next Blockchain generation decided to improve on the first generation. This generation took a huge leap forward by creating a Turing complete blockchain(a system that could process and solve any logically complete computational problem). Simply put, it built a computer into the blockchain, so now users aren't restricted to just making transactions, but rather their imaginations on what programs they could build on the computer. They created programs compatible with the blockchain using smart contracts. Smart contracts are programs stored on a blockchain that run when predetermined conditions are met.
One notable chain in this generation is the Ethereum chain, which is not Turing complete, but Quasi-Turing complete instead, this means that all execution processes are limited to a finite number of computational steps(simply put, it won't execute a program that would run forever). With Ethereum, smart contracts became a thing, which then birthed a whole ecosystem of programs, utilities and communities. This includes the developments of tokens(fungible and non-fungible), which themselves are a type of smart contracts, decentralized autonomous organizations(DAOs), Oracles, etcetera, the list is endless.
This innovation quickly made Ethereum a hub for many applications (Decentralized Apps), but this rapid growth on Ethereum came at a cost and the chain almost immediately began to suffer from scaling problems.

ETHEREUM
The scaling issues with Ethereum quickly lead to different developers rushing to come up with different solutions. Most solutions are divided into two sections, on-chain(Layer1) solutions and off-chain(Layer2) solutions. I wrote an article covering the subject.
Much of the talk on the second generation has been on Ethereum, while it is not the only chain in this category, one of its co-founders Vitalik Buterin was the individual that popularized the idea of a blockchain that was computationally capable.
NEO
Neo launched as antshares in 2014, it was created by Da Hongfei and Erick Zhang, and it was later rebranded to Neo in 2017. Neo is a platform on top of which anyone can transact and create decentralized products and services with its NeoContracts. It is sometimes referred to as the “Ethereum of China”. NeoContracts is quite different in the sense that developers can build applications on it using existing languages (like C# and Java), rather than learning a new language like Solidity or Vyper used to write Ethereum's smart contracts.
More recent chains that do what Ethereum does now would include, Solana, Avalanche, Fantom and Ethereum Classic.
Third Generation Blockchains
The present blockchain generation took another step forward, bringing, improvements, efficiency, scalability and interoperability to the blockchain realms. One of the major issues facing blockchain is scaling, Bitcoin remains troubled by its slow transaction processing time and bottlenecks. Ethereum users also suffer from high transaction costs from its gas payment infrastructure defeating the promise of being cheap and accessible to everyone. Many new blockchains have attempted to solve these problems with varying levels of success. The attempts of making chains scalable, interoperable and cheap ushered in the new generation.
Some of the blockchains with that goal and drive at the forefront of solving the problems include, Cardano and Polkadot, both of whose creators were formerly Ethereum's Co-founders. It's a trail of Ethereum everywhere.
CARDANO
Cardano can already process thousands of transactions per second using their Hydra node system. It can also scale to making millions of transactions per second if the need arises. It runs on a proof-of-stake consensus algorithm, bringing power usage and efficiency to the game. Transaction costs are also very low in cents. Confirmation time is also within minutes. Though it did not start out having smart contracts built in, an upgrade happened in late 2021 that brought in the feature.
POLKADOT
Polkadot can also process thousands of transactions per second with the possibility of scaling up to millions like Cardano. It also operates on a proof-of-stake consensus algorithm. Polkadot's ecosystem is more developed than Cardano’s ecosystem currently, with projects such as Kusama and Ocean Protocol already on the blockchain. Its development is going rapidly which is what the space needs. Polkadot was started by Gavin Wood, the same guy that created solidity, wrote the first set of testnets on Ethereum and lead the team that wrote the Parity Ethereum software client, written in Rust.
There is still a lot coming up ahead, that we have no idea of or how it would impact our everyday life, but as long as our needs from this technology continue to increase, the technology would continuously improve and keep up as well.
What a time to be alive!